Source: pixabay.com
Introduction: Data-centric networking (DCN) marks a significant change in the approach to networking. Unlike traditional models which are host-centric, DCN is more data-centric. DCN shifts the emphasis from the data’s location, such as IP address, to the content, enhancing routing, storage, data querying, and overall efficiency.
As the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and extensive data distribution systems develop, DCN seems to emerge as one of the core fundamentals of modern networking. This guide focuses on data-centric networking, outlining its theories, concepts, examples, benefits, challenges, applications, and future opportunities.
1. Understanding Data-Centric Networking
1.1 What is Data-Centric Networking (DCN)?
Data-centric networking (DCN) is an approach to networking that emphasizes data rather than host addresses. Unlike previous models that relied on data-centric routing and host adjacency through IP addresses, DCN focuses on how data is named, stored, and even distributed in large-scale networks.
Distinguished Features of DCN:
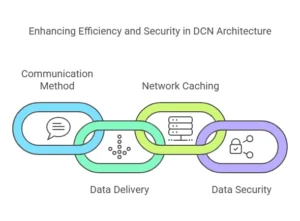
🔹 Communication- based on the contents versus content-based. Information retrieved is obtained via the name of the data and not the location.
🔹 Optimal Delivery of Data – The network uses the shortest route to deliver the data needed.
🔹 Caching & Storage In-Network—Data is stored in the network, which helps ensure redundancy and lowers network load.
🔹 Security at the Data Level – Makes sure the data itself is secured and can easily be verified.
2. How Data-Centric Networking Differs from Traditional Networking?
| Feature | Data-Centric Networking (DCN) | Traditional Networking (Host-Centric) |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Focus | Data itself | Host addresses (IP-based) |
| Routing Mechanism | Content-based routing | IP-based routing |
| Efficiency | Caching and replication reduce redundancy | Data requests must go through specific paths |
| Security | Embedded in data | Secured through network protocols |
| Examples | Named Data Networking (NDN), Content-Centric Networking (CCN) | TCP/IP-based networks |
In DCN, users can make content requests like video files, research documents, or sensor data, and the content will be fetched from the closest point of access to the user, which can either be the actual provider or a cached version.
3. Technologies Underpinning Data-Centric Networking
3.1 Named Data Networking (NDN)
NDN is an operational form of data-centric networking that eliminates the use of IP addresses and instead uses unique identifiers as names for data.
🔹 Use case: With video streaming, users make requests for videos instead of requesting them from particular servers. The network retrieves and provides the video from the closest data point/store.
3.2 Content-Centric Networking (CCN)
CCN is another model of DCN that involves the locating and retrieving of data by its content- the name of the content instead of the location on the server.
🔹 Use case: A document may be searched for from a certain server, but in reality, the user places an order/request using the document name. The network as a whole delivers and fetches the document from a cache, not a specific server.
4. Use Cases of Data-Centric Networking
4.1 Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN)
In WSNs, data is captured from several sensors and forwarded to a central node. Advantage of DCN is in routing the data to eliminate the unnecessary transfer of information by only sending relevant details.
For Example:
Smart Traffic Management – Smart Traffic Management Systems process sensor data and receive live updates concerning the movement of vehicles. The processed information is relevant, so there is sent data traffic is unnecessary raw data.
4.2 Information-Centric Networking (ICN)
ICN is an overarching framework that incorporates DCN. It aims at reducing the extent of Internet usage and enhancing scalability and security by regarding content as the principal element rather than devices.
For Example:
Global Data Distribution – Principles of ICN are put into practice in the distribution of video content by Companies such as Netflix and YouTube that serve the video from the nearest cache location reducing the load on the server.
5. Benefits of Data-Centric Networking
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Efficiency | Data caching reduces redundant requests, lowering bandwidth usage. |
| Scalability | Handles a growing number of devices and data sources effectively. |
| Security | Embeds security directly into data rather than relying on network-level encryption. |
| Reduced Latency | Delivers data from the nearest available cache, speeding up access. |
6. Challenges and Limitations of Data-Centric Networking
6.1 Infrastructure Transition
Most existing networks are built on IP-based architectures, making it difficult to shift to a fully DCN-based system.
6.2 Naming & Indexing Complexity
Unlike IP addresses, which follow a structured format, naming data uniquely in DCN requires an advanced indexing system.
6.3 Storage Overhead
Because DCN relies on in-network caching, storage demands increase significantly as more content is cached.
6.4 Security Risks
Although DCN improves security, attackers can exploit caching mechanisms to inject malicious content.
7. Prospects of Data-Centric Networking
Link with 5th Gen Networks – Ultra high-speed content delivery will be improved with DCN in 5G and further generations.
AI and ML – With the use of AI, powered DCN will be able to foresee data requirements and streamline the network.
Advanced IoT and Smart Cities Development – Smart DCN will be increasingly adopted for real-time data exchange.
8. The Importance of Data-Centric Networking in Edge Computing
With the emergence of edge computing, DCN is fundamental in further improving the latency and data delivery at the edge. Unlike traditional networks that depend on cloud data centers, DCN allows data to be processed locally by fetching information from the nearest source. This improves analytics, network congestion, and the overall quality of real-time IoT applications, autonomous vehicles, and smart grids.
Self-driving cars, for instance, need real-time navigation data processing. DCN allows vehicles to fetch road condition data from the nearest edge nodes instead of having it sent from a remote cloud server which boosts safety and efficiency.
9. How Data-Centric Networking alter the Cybersecurity Perspective?
In modern networks, security is always a primary issue and in this regard, DCN has an advantage. In contrast to traditional networks that focus on securing communication channels, DCN focuses on securing the data itself. This strategy minimizes risks related to man-in-the-middle attacks and DDoS threats. As with any new technology, DCN creates additional problems, such as how to maintain the authenticity and integrity of data stored in distributed caches. New methods of access control like blockchain-based authentication or more sophisticated encryption are being developed to secure DCN.
10. How does DCN Improves Cloud Computing And Big Data Processing?
The proliferation of big data has made it particularly difficult for cloud platforms to handle transferring vast amounts of data. By minimizing redundant data transfers and improving access speeds via content caching, DCN enhances cloud environments.
In clustered cloud systems, for instance, DCN allows for distributed content delivery across various data centers, improving data consistency while alleviating server strain. Large-scale data analytics firms like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft are migrating towards DCN-based frameworks to better control data stream management.
11. The Development of Data-Centric Networking In 6G And Beyond
Research on 6G has already begun, even while 5G infrastructure is being implemented around the globe. One of the primary features of 6G DCN will address is going to be networking. 6G Infrastructure is designed to facilitate an ultra-smart, hyper-connected environment with data-centric communications taking the place of host-based.
Some of the innovations in 6G that we can expect DCN to drive are:
✔ AI-based adaptive streaming or intelligent content delivery.
✔ Need for low-latency data transmission for holographic communications.
✔ Concepts of quantum networking with integration of DCN security principles.
With billions of devices connected, the need for data communication becomes exponentially greater. This is where the development of 6G will require DCN to be essential.
12. Problems with Implementing Data-Centric Networking Globally
Network-centric data management has many advantages; however, the world’s adoption of it suffers from numerous problems. The backward compatibility with existing IP-based networks is the biggest concern. Moving from host-centric to data-centric architectures requires significant changes in the networks’ infrastructure, policies, and even business frameworks.
Some other significant problems are:
✔ Standardization Problems – DCN does not offer a uniform model, which leads to various DCN implementations.
✔ Regulatory Issues – Existing frameworks allow ISPs and governments to control the data traffic, and moving to a DCN model needs too many changes in policies.
✔ Complexity of Data Naming – Billions of unique content names need to be indexed using advanced techniques.
Even with all these problems, further research alongside industry partnerships is heading toward a uniformly scalable DCN implementation that can be reliably defended.
Conclusion
Data-centric networking (DCN) is revolutionizing modern communication by making data easier to access, store, and distribute. As technologies like 5G, IoT, and AI continue to grow, DCN will play a critical role in the future of networking.
FAQs
1. What is the main goal of Data-Centric Networking?
DCN aims to optimize data retrieval, storage, and security by focusing on content rather than device addresses.
2. How does DCN improve data security?
Security is embedded within data using encryption, ensuring safer transmission even in untrusted environments.
3. Is Data-Centric Networking better than traditional IP networking?
DCN offers efficiency, scalability, and security, but IP-based networks remain dominant due to existing infrastructure.
4. Where can I find Data-Centric Networking study materials (PDF, PPT, Notes)?
📌 PDFs & Research Papers – Available on Google Scholar, IEEE, and ACM Digital Library.
📌 PPT Slides – Check SlideShare, university websites, and conference proceedings.
📌 Notes & Tutorials – Found on GitHub, ResearchGate, and academic forums.